XStream开发指南¶
本文将Step by step介绍如何基于XStream完成一个业务场景下的SDK的开发
Method开发¶
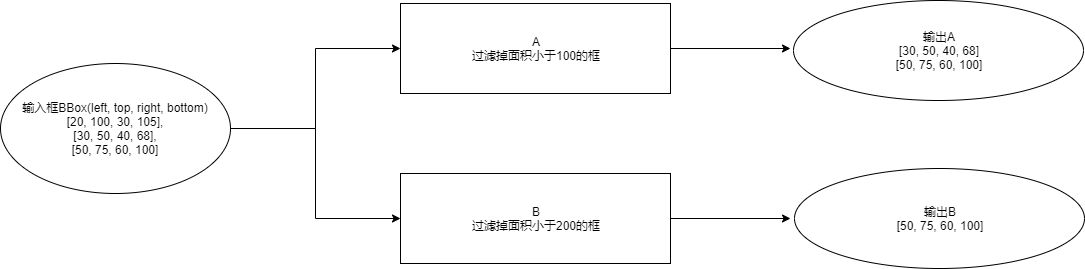
根据上面的功能描述,需要实现一个根据面积过滤框的Method,命名为BBoxFilter。
1. 定义数据类型¶
BBoxFilter Method需要输入一组BBox,输出一组BBox,因此需要定义的数据类型为BBox。
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/method/b_box.h
namespace hobot {
namespace vision {
template <typename Dtype>
struct BBox_ {
inline BBox_() {}
inline BBox_(Dtype x1_, Dtype y1_, Dtype x2_, Dtype y2_, float score_ = 0.0f,
int32_t id_ = -1, const std::string &category_name_ = "") {
x1 = x1_;
y1 = y1_;
x2 = x2_;
y2 = y2_;
id = id_;
score = score_;
category_name = category_name_;
}
inline Dtype Width() const { return (x2 - x1); }
inline Dtype Height() const { return (y2 - y1); }
inline Dtype CenterX() const { return (x1 + (x2 - x1) / 2); }
inline Dtype CenterY() const { return (y1 + (y2 - y1) / 2); }
Dtype x1 = 0;
Dtype y1 = 0;
Dtype x2 = 0;
Dtype y2 = 0;
float score = 0.0;
int32_t id = 0;
std::string category_name = "";
};
typedef BBox_<float> BBox;
}
Note: 为了统一基础数据结构定义,我们在vision_type中预定义了一组基础数据类型,包括检测框BBox、关键点Landmark、人脸3DPose信息、基础图像帧表示等,你可以直接复用,详细参考xstream/vision_type目录。
2. 数据类型封装¶
基于XStreamData将自定义数据类型需要封装为在XStream数据表示,从而支持在XStream中流转。
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/method/b_box.h
typedef XStreamData<hobot::vision::BBox> BBox;
输入输出是一组BBox,因此是一个BaseDataVector, 构成一个BBox数组的方式为:
BaseDataVector *data(new BaseDataVector);
xstream::BBox *bbox1(new hobot::vision::BBox(20, 100, 30, 105));
bbox1->type_ = "BBox";
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox1));
xstream::BBox *bbox2(new hobot::vision::BBox(5, 50, 60, 68));
bbox2->type_ = "BBox";
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox2));
3. Method实现¶
继承Method基类,实现BBoxFilter Method
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/method/b_box_filter.h
#include "hobotxstream/method.h"
namespace xstream {
class BBoxFilter : public Method {
public:
// 价值json配置参数,完成method初始化
int Init(const std::string &config_file_path) override;
// 数据处理函数,第一个参数是输入数据(双重vector,外层vector表示batch是多帧的输入
// 内层的vector表示单帧的数据列表),
// Note:由于目前XStream框架接口并没有支持Batch模式,外层的vector恒等于1
std::vector<std::vector<BaseDataPtr>> DoProcess(
const std::vector<std::vector<BaseDataPtr>> &input,
const std::vector<xstream::InputParamPtr> ¶m) override;
// 析构
void Finalize() override {}
// 动态改变Method运行参数配置
int UpdateParameter(InputParamPtr ptr) override;
// 获取Method运行参数配置
InputParamPtr GetParameter() const override;
// 获取Method版本号,比如 metric_v0.4.0 或者 MD112 等
std::string GetVersion() const override {
return "BBoxFilter_test_v0.0.1";
}
// 当workflow的profile状态发生变化时,调用该函数.
void OnProfilerChanged(bool on) override {}
private:
// 过滤bbox的面积阈值
std::atomic<float> area_threshold_;
};
} // namespace xstream
DoProcess:根据面积过滤框,这里没有直接过滤掉框,而是设置了Filter状态,最终输出可以通过检查状态位得到剩余框(未被过滤的框状态应为VALID):
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/method/b_box_filter.cc
std::vector<std::vector<BaseDataPtr>> BBoxFilter::DoProcess(
const std::vector<std::vector<BaseDataPtr>> &input,
const std::vector<InputParamPtr> ¶m) {
std::cout << "BBoxFilter::DoProcess" << std::endl;
std::vector<std::vector<BaseDataPtr>> output;
output.resize(input.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < input.size(); ++i) {
// 当前不支持batch模式,batch恒等于1
assert(i <= 1);
auto &in_batch_i = input[i];
auto &out_batch_i = output[i];
out_batch_i.resize(in_batch_i.size());
std::cout << "input size: " << in_batch_i.size() << std::endl;
// 只支持n个输入,输入格式是BBox的数组
for (size_t j = 0; j < in_batch_i.size(); ++j) {
auto in_rects = std::static_pointer_cast<BaseDataVector>(in_batch_i[j]);
assert("BaseDataVector" == in_rects->type_);
auto out_rects = std::make_shared<BaseDataVector>();
out_batch_i[j] = std::static_pointer_cast<BaseData>(out_rects);
for (auto &in_rect : in_rects->datas_) {
auto bbox = std::static_pointer_cast<xstream::BBox>(in_rect);
// 因为BBoxFilter_A和BBoxFilter_B使用智能指针指向同一份输入数据,为避免两个Filter在一个处理完成后修改State,
// 影响另一个Filter处理输入数据,这里会将原来的输入数据copy一份
auto out_rect = BaseDataPtr(new xstream::BBox(bbox->value));
out_rect->type_ = bbox->type_;
// 如果已经被之前的模块过滤掉,直接传递到输出。
if (in_rect->state_ == DataState::FILTERED) {
out_rects->datas_.push_back(in_rect);
continue;
}
assert("BBox" == out_rect->type_);
if (bbox->value.Width() * bbox->value.Height() > area_threshold_) {
out_rects->datas_.push_back(out_rect);
} else {
std::cout << "B filter: " << bbox->value.x1 << "," << bbox->value.y1
<< "," << bbox->value.x2 << "," << bbox->value.y2
<< std::endl;
// 设置过滤状态,输出通过该状态过滤
out_rect->state_ = DataState::FILTERED;
out_rects->datas_.push_back(out_rect);
}
}
}
}
return output;
}
初始化时需要解析json配置参数,初始化不同的阈值,对模块A需要过滤掉面积小于100的框,a_filter.json配置为:
{
"threshold" : 100
}
b_filter.json配置为:
{
"threshold" : 200
}
需要注意的是Init输入参数为Json config文件路径,并不是json配置文件本身,需要先load文件然后完成json解析:
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/method/b_box_filter.cc
int BBoxFilter::Init(const std::string &config_file_path) {
std::ifstream infile(file_path);
Json::Value cfg_jv;
infile >> cfg_jv;
infile.close();
area_threshold_ = cfg_jv["threshold"].asFloat();
return 0;
}
如果需要运行时更新阈值,需要实现UpdateParameter
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/method/b_box_filter.cc
int BBoxFilter::UpdateParameter(InputParamPtr ptr) {
auto real_ptr = dynamic_cast<xstream::FilterParam *>(ptr.get());
if (real_ptr->HasThreshold()) {
area_threshold_ = real_ptr->GetThreshold();
}
return 0;
}
UpdateParameter的输入参数类型是InputParamPtr,这是XStream定义的参数类型的基类,用户需要继承该基类实现自定义的输入参数类FilterParam:
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/filter_param.h
#include "hobotxsdk/xstream_data.h"
namespace xstream {
typedef struct _FilterParam__isset {
_FilterParam__isset() : threshold(false) {}
bool threshold : 1;
} _FilterParam__isset;
class FilterParam : public InputParam {
public:
explicit FilterParam(std::string unique_name) : InputParam(unique_name) {
threshold_ = 2500.0;
}
virtual ~FilterParam() = default;
virtual std::string Format() {
return std::string("threshold") + std::to_string(threshold_);
}
void SetThreshold(float thres) {
threshold_ = thres;
is_set_.threshold = true;
}
bool HasThreshold() { return is_set_.threshold; }
float GetThreshold() { return threshold_; }
private:
_FilterParam__isset is_set_;
float threshold_;
};
} // namespace xstream
Workflow构建¶
filter_workflow.json文件内容如下:
{
"inputs":[
"in_bbox"
],
"outputs":[
"bbox_filtered_A",
"bbox_filtered_B"
],
"workflow":[
{
"method_type":"BBoxFilter",
"unique_name":"BBoxFilter_A",
"inputs":[
"in_bbox"
],
"outputs":[
"bbox_filtered_A"
],
"method_config_file":"a_filter.json"
},
{
"method_type":"BBoxFilter",
"unique_name":"BBoxFilter_B",
"inputs":[
"in_bbox"
],
"outputs":[
"bbox_filtered_B"
],
"method_config_file":"b_filter.json"
}
]
}
上面的配置文件对应的workflow如下图: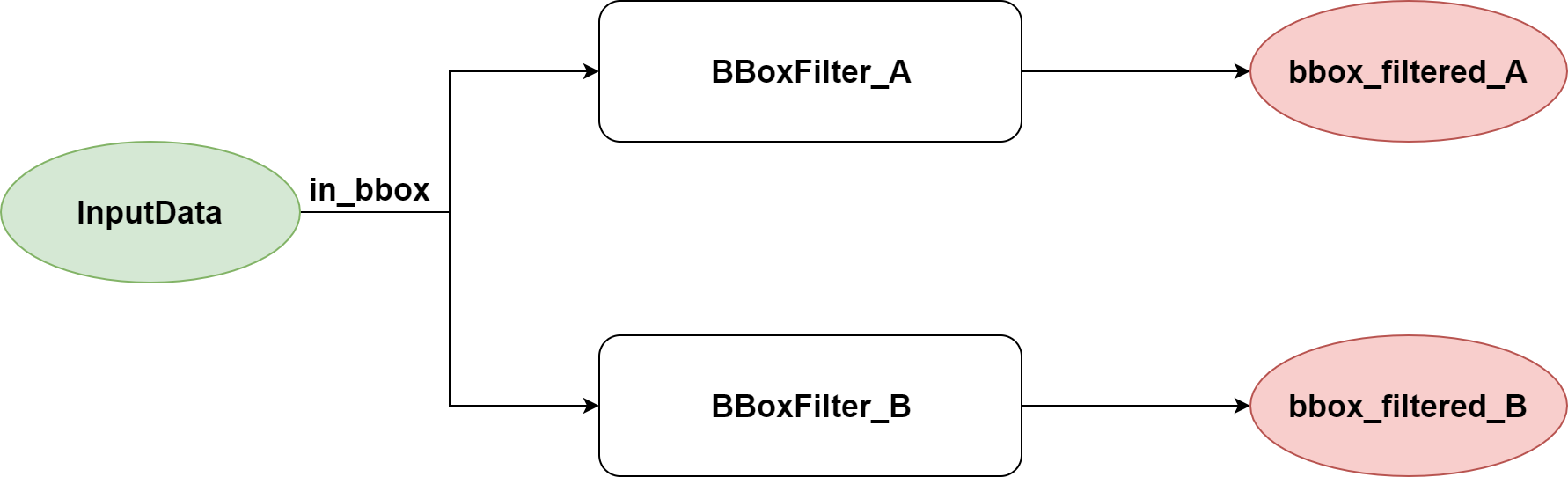
SDK集成¶
1. 测试数据准备¶
InputDataPtr inputdata(new InputData());
BaseDataVector *data(new BaseDataVector);
xstream::BBox *bbox1(new xstream::BBox(
hobot::vision::BBox(20, 100, 30, 105)));
xstream::BBox *bbox2(new xstream::BBox(
hobot::vision::BBox(40, 50, 60, 68)));
xstream::BBox *bbox3(new xstream::BBox(
hobot::vision::BBox(50, 75, 60, 100)));
bbox1->type_ = "BBox";
bbox2->type_ = "BBox";
bbox3->type_ = "BBox";
std::cout << "bbox1: " << bbox1->value << std::endl;
std::cout << "bbox2: " << bbox2->value << std::endl;
std::cout << "bbox3: " << bbox3->value << std::endl;
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox1));
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox2));
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox3));
data->name_ = "in_bbox";
inputdata->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(data));
如上面章节说明XStream框架中流转的数据需要基于一个公共基类BaseData扩展,产生输入数据时也需要把输入数据先转化为XStream数据表示。 这里做了两次转化:
将基础数据类型hobot::vision::BBox转化为带XStream描述信息的表示:
xstream::BBox *bbox1(new xstream::BBox(
hobot::vision::BBox(20, 100, 30, 105)));
xstream::BBox *bbox2(new xstream::BBox(
hobot::vision::BBox(40, 50, 60, 68)));
xstream::BBox *bbox3(new xstream::BBox(
hobot::vision::BBox(50, 75, 60, 100)));
// 添加数据类型描述信息
bbox1->type_ = "BBox";
bbox2->type_ = "BBox";
bbox3->type_ = "BBox";
xstream::BBox的定义为:
typedef XStreamData<hobot::vision::BBox> BBox;
Workflow的输入数据为一组框,因此需要把上述3个BBox定义组织到数组中,同时数组也要转化为XStream数据表示: BaseData的数组表示为BaseDataVector, BaseDataVector已经是BaseData的子类,可以直接转化为BaseData。
BaseDataVector *data(new BaseDataVector);
...
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox1));
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox2));
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox3));
// 数据的name, 需要和定义的json workflow的输入部分name一致
data->name_ = "in_bbox";
这里需要注意的是输入数据需要添加name信息,name需要和定义的JSON workflow inputs一样,预测时即是通过该信息Feed workflow:
{
"inputs":[
"in_bbox"
],
"outputs":[
"bbox_filtered_A",
"bbox_filtered_B"
]
}
XStream输入数据的数据结构为:
// 输入数据类型
struct InputData {
// 用户输入的数据,比如图片channel、时间戳、框等等
std::vector<BaseDataPtr> datas_;
// 当前请求自定义的参数
std::vector<InputParamPtr> params_;
// 数据源 id 用于多路输入时区分输入源,单一源情况赋值为 0
uint32_t source_id_ = 0;
// 透传的数据,该数据会透传到OutputData::context_ 字段
const void *context_ = nullptr;
};
输入数据存储在datas_中:
data->name_ = "in_bbox";
inputdata->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(data));
2. Method注册¶
XStream框架构建workflow时,调用全局MethodFactory创建对应Method实例,在使用BBoxFilter之前需要注册到MethodFactory中;
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/method_factory.h
#include "hobotxstream/method_factory.h"
#include "method/bbox_filter.h"
namespace xstream {
MethodPtr MethodFactory::CreateMethod(const std::string &method_name) {
if ("BBoxFilter" == method_name) { // method_name即为JSON config中Node @method_type 名字。
return MethodPtr(new BBoxFilter());
} else {
return MethodPtr();
}
}
} // namespace xstream
3. 同步预测¶
调用XStreamSDK的class静态接口CreateSDK, 创建一个XStreamSDK的对象,并使用SyncPredict进行同步预测。
构建SDK代码如下:
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/sync_main.cc文件对输入数据稍作改动,改成了循环输入10次数据。
using xstream::BaseData;
using xstream::BaseDataPtr;
using xstream::BaseDataVector;
using xstream::InputData;
using xstream::InputDataPtr;
if (argc < 2) {
std::cout << "Usage : ./bbox_filter_main work_flow_config_file"
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Example : ./bbox_filter_main ./filter_workflow.json"
<< std::endl;
return -1;
}
auto config = argv[1];
xstream::XStreamSDK *flow = xstream::XStreamSDK::CreateSDK();
flow->SetConfig("config_file", config);
flow->Init();
float x1{0}; // BBox(框)的左上角横坐标
float y1{20}; // BBox(框)的左上角纵坐标
float x2{0}; // BBox(框)的右上角横坐标
float y2{50}; // BBox(框)的右上角纵坐标
// 框的面积计算公式:(x2-x2)*(y2-y1)
if (argc == 2) {
std::cout << "***********************" << std::endl
<< "testing synchronous function" << std::endl
<< "***********************" << std::endl;
// 生成面积为{ 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, 240,
// 270 } 序列,作为BBoxFilter的输入数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
x2 = i;
InputDataPtr inputdata(new InputData());
BaseDataVector *data(new BaseDataVector);
xstream::BBox *bbox(
new xstream::BBox(hobot::vision::BBox(x1, y1, x2, y2)));
bbox->type_ = "BBox";
std::cout << "main i:" << i << " bbox:" << bbox->value << std::endl;
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox));
data->name_ = "in_bbox";
inputdata->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(data));
auto out = flow->SyncPredict(inputdata);
ParseOutput(out);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
}
}
delete flow;
同步预测接口SyncPredict,传⼊输入数据后,接口会阻塞住,直到整个workflow处理完成,将workflow的结果通过函数返回值返回为⽌。该接口需要在Init()之后执⾏才有效。
4. 异步预测¶
调用XStreamSDK的class静态接口CreateSDK, 创建一个XStreamSDK的对象,并使用AsyncPredict进行异步预测。
其中涉及以下两个接口:
接口:
virtual int64_t AsyncPredict(InputDataPtr input) = 0;
说明:异步预测接口,AsyncPredict接⼝调⽤后立即返回,结果通过SetCallback设置的回调函数捕获。
Note:该接⼝需要在Init()之后执⾏才有效。
设置异步回调接口
virtual int SetCallback(XStreamCallback callback, const std::string &name = "") = 0;
说明:使⽤异步分析接口时,设置SetCallback才有效。 将name设置为默认值,通过该接口可以设置整个workflow处理完成后的回调函数; 将name设置为某个Node的unique名字,通过该接口可以设置某个method实例处理完成后的回调函数。
基于异步接口创建sdk的方式:
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/async_main.cc
using xstream::BaseData;
using xstream::BaseDataPtr;
using xstream::BaseDataVector;
using xstream::InputData;
using xstream::InputDataPtr;
using Stage1Async::Callback;
if (argc < 2) {
std::cout << "Usage : ./bbox_filter_main work_flow_config_file"
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Example : ./bbox_filter_main ./filter_workflow.json"
<< std::endl;
return -1;
}
auto config = argv[1];
xstream::XStreamSDK *flow = xstream::XStreamSDK::CreateSDK();
Callback callback;
// 整个Workflow回调函数
flow->SetCallback(
std::bind(&Callback::OnCallback, &callback, std::placeholders::_1));
flow->SetConfig("config_file", config);
flow->Init();
// BBoxFilter_A回调函数
flow->SetCallback(
std::bind(&Callback::OnCallback, &callback, std::placeholders::_1),
"BBoxFilter_A");
// BBoxFilter_B回调函数
flow->SetCallback(
std::bind(&Callback::OnCallback, &callback, std::placeholders::_1),
"BBoxFilter_B");
// Get Method Version
std::cout << "BBoxFilter_A Method Version : "
<< flow->GetVersion("BBoxFilter_A") << std::endl;
float x1{0}; // BBox(框)的左上角横坐标
float y1{20}; // BBox(框)的左上角纵坐标
float x2{0}; // BBox(框)的右上角横坐标
float y2{50}; // BBox(框)的右上角纵坐标
// 框的面积计算公式:(x2-x2)*(y2-y1)
if (argc == 2) {
std::cout << "***********************" << std::endl
<< "testing synchronous function" << std::endl
<< "***********************" << std::endl;
// 生成面积为{ 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, 240,
// 270 } 序列,作为BBoxFilter的输入数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
x2 = i;
InputDataPtr inputdata(new InputData());
BaseDataVector *data(new BaseDataVector);
xstream::BBox *bbox(
new xstream::BBox(hobot::vision::BBox(x1, y1, x2, y2)));
bbox->type_ = "BBox";
std::cout << "i:" << i << " bbox:" << bbox->value << std::endl;
data->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(bbox));
data->name_ = "in_bbox";
inputdata->datas_.push_back(BaseDataPtr(data));
auto out = flow->AsyncPredict(inputdata);
// waiting for async function done
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
}
}
delete flow;
定义和设置 callback:
定义用户的Callback类,实现一个类似OnCallback函数,参数类型为
xstream::OutputDataPtr output,用来处理XStream worflow的回调结果。代码:class Callback { public: void OnCallback(xstream::OutputDataPtr output) { ParseOutput(output); } };
设置callback
Callback::Callback callback; flow->SetCallback( std::bind(&MethodCallback::Callback::OnCallback, &callback, std::placeholders::_1));
5. 预测结果解析¶
// xstream/tutorials/stage1/sync_main.cc
void ParseOutput(xstream::OutputDataPtr output) {
using xstream::BaseDataVector;
std::cout << "=====================" << std::endl;
std::cout << "seq: " << output->sequence_id_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "output_type: " << output->output_type_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "method_unique_name: " << output->unique_name_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "error_code: " << output->error_code_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "error_detail_: " << output->error_detail_ << std::endl;
std::cout << "datas_ size: " << output->datas_.size() << std::endl;
for (auto data : output->datas_) {
if (data->error_code_ < 0) {
std::cout << "data error: " << data->error_code_ << std::endl;
continue;
}
std::cout << "data type_name : " << data->type_ << " " << data->name_
<< std::endl;
BaseDataVector *pdata = reinterpret_cast<BaseDataVector *>(data.get());
std::cout << "pdata size: " << pdata->datas_.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "Output BBox " << pdata->name_ << ":";
for (size_t i = 0; i < pdata->datas_.size(); ++i) {
auto xstream_box =
std::static_pointer_cast<xstream::XStreamData<hobot::vision::BBox>>(
pdata->datas_[i]);
if (xstream_box->state_ == xstream::DataState::VALID) {
std::cout << "[" << xstream_box->value.x1 << "," << xstream_box->value.y1
<< "," << xstream_box->value.x2 << "," << xstream_box->value.y2
<< "]" << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
输出数据结构为:
// xstream/framework/include/hobotxsdk/xstream_data.h
// 输出数据类型
struct OutputData {
// 错误码
int error_code_ = 0;
// 错误信息
std::string error_detail_ = "";
// 当该OutputData为给某个Method的定向回调结果时,该字段用于指示Method名称
std::string unique_name_ = "";
// 多路输出结果名称
std::string output_type_ = "";
// 输出结果
std::vector<BaseDataPtr> datas_;
// 从InputData透传过来的数据
const void *context_ = nullptr;
// 该结果的序列号
int64_t sequence_id_ = 0;
// 该结果是属于那个输入源产生的结果
uint32_t source_id_ = 0;
uint64_t global_sequence_id_ = 0;
};
typedef std::shared_ptr<OutputData> OutputDataPtr;
datas_字段存储了输出的结果,对于该workflow保护两个输出:
{
"inputs": ["in_bbox"], // 输入的数据list,它是workflow里面定义的inputs的子集
"outputs": ["bbox_filtered_A",
"bbox_filtered_B"], // 输出的数据list,它是workflow里面定义的outputs的一个子集
...
每个输出都是一个框的数组,解析的数据结果层次为:
std::vector<BaseDataPtr>
--> BaseDataPtr(BaseDataVector)
--> BaseDataPtr(std::shared_ptr<XStreamData<hobot::vision::BBox>>)
--> xstream_data->value_(hobot::vision::BBox);
6. 动态更新配置¶
如果想动态更新BBoxFilter的阈值,可以调用UpdateConfig接口完成。
接口
virtual int UpdateConfig(const std::string &unique_name, InputParamPtr ptr) = 0;
说明:用于设置method的参数,最终会通过调用对应的Method->UpdateParameter(InputParamPtr ptr)接口,完成Method参数的更新。
@unique_name:指定需要更新配置的node的unique name;
@ptr:需要更新配置信息
调用GetConfig可以获得Node当前参数配置。
接口
virtual InputParamPtr GetConfig(const std::string &unique_name) const = 0;
说明:获取某个method的参数,最终会调用对应的Method->GetParameter()返回method配置信息。
代码
std::cout << "***********************" << std::endl
<< "testing aysnc function" << std::endl
<< "***********************" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
flow->AsyncPredict(inputdata);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
if (i == 5) {
std::string unique_name("BBoxFilter_A");
auto ptr = std::make_shared<xstream::FilterParam>(unique_name);
ptr->SetThreshold(90.0);
flow->UpdateConfig(ptr->unique_name_, ptr);
}
}
auto node_config = flow->GetConfig("BBoxFilter_A");
if (node_config) {
auto real_ptr = dynamic_cast<xstream::FilterParam *>(node_config.get());
std::cout << "threshold:" << real_ptr->GetThreshold() << std::endl;
}